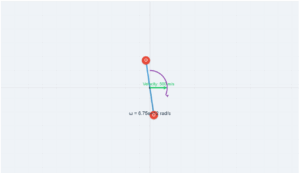
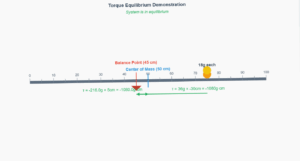
Torque Vector Visualization
Interactive 3D representation of torque as the cross product of position and force vectors
Example
Question:
Find the torque of a force \( \mathbf{F} = 7\mathbf{\hat{i}} + 3\mathbf{\hat{j}} - 5\mathbf{\hat{k}} \) about the origin.
The force acts on a particle whose position vector is \( \mathbf{r} = \mathbf{\hat{i}} - \mathbf{\hat{j}} + \mathbf{\hat{k}} \).
Solution:
We use the cross product \( \mathbf{\tau} = \mathbf{r} \times \mathbf{F} \):
\[
\mathbf{\tau} =
\begin{vmatrix}
\mathbf{\hat{i}} & \mathbf{\hat{j}} & \mathbf{\hat{k}} \\
1 & -1 & 1 \\
7 & 3 & -5 \\
\end{vmatrix}
\]
Calculate each component:
\[
\mathbf{\tau} =
( -1 \times -5 - 1 \times 3 ) \mathbf{\hat{i}}
- ( 1 \times -5 - 1 \times 7 ) \mathbf{\hat{j}}
+ ( 1 \times 3 - ( -1 \times 7 ) ) \mathbf{\hat{k}}
\]
\[
= (5 - 3)\,\mathbf{\hat{i}} - ( -5 - 7 )\,\mathbf{\hat{j}} + ( 3 + 7 )\,\mathbf{\hat{k}}
\]
\[
= 2\mathbf{\hat{i}} + 12\mathbf{\hat{j}} + 10\mathbf{\hat{k}}
\]
Final Answer:
\( \mathbf{\tau} = 2\mathbf{\hat{i}} + 12\mathbf{\hat{j}} + 10\mathbf{\hat{k}} \)
Physics Explanation
Torque (τ) is calculated as the cross product of the position vector (r) and force vector (F):
Given the initial vectors: