Enhanced 3D Raindrop Physics Simulation
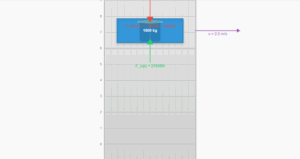
This enhanced 3D visualization demonstrates a raindrop falling under gravity with air resistance, featuring realistic physics, beautiful lighting, and interactive controls. Based on Example 6.2 from the textbook.
Height
1000 m
Velocity
0 m/s
Time
0.00 s
Kinetic Energy
0.00 J
Air Resistance
0.00 N
Gravity (Fg)
Air Resistance (Fr)
Raindrop
Net Force
Physics Explanation
Question:
It is well known that a raindrop falls under the influence of the downward gravitational force and the opposing resistive force (proportional to speed). Consider a drop of mass 1.00 g falling from a height 1.00 km. It hits the ground with a speed of 50.0 m/s.
(a) What is the work done by the gravitational force?
(b) What is the work done by the unknown resistive force?
Work done by gravity (Wg):
Wg = mgh = (10-3 kg)(10 m/s²)(1000 m) = 10.0 J
Wg = mgh = (10-3 kg)(10 m/s²)(1000 m) = 10.0 J
Final kinetic energy (ΔK):
ΔK = ½mv² = ½(10-3 kg)(50 m/s)² = 1.25 J
ΔK = ½mv² = ½(10-3 kg)(50 m/s)² = 1.25 J
Work done by air resistance (Wr):
From work-energy theorem: ΔK = Wg + Wr
Wr = ΔK - Wg = 1.25 J - 10.0 J = -8.75 J
From work-energy theorem: ΔK = Wg + Wr
Wr = ΔK - Wg = 1.25 J - 10.0 J = -8.75 J
The negative sign indicates the resistive force opposes the motion.
Visualization Notes
This enhanced visualization shows:
- Realistic raindrop shape with surface tension effects
- Dynamic lighting that changes with the drop's position
- Force vectors that scale with magnitude
- Optional rain effect to show environmental context
- Camera follow mode to track the raindrop