Bubble Pressure Simulation
Visualizing pressure differences in soap bubbles and air bubbles within a liquid
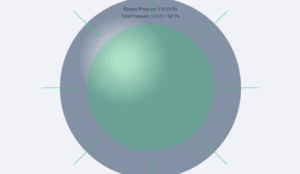
Soap Bubble Pressure
Excess pressure inside soap bubble
P = 4S/r
Air Bubble Pressure
Total pressure inside air bubble
P = P₀ + hρg + 2S/r
Pressure Components
Atmospheric pressure (P₀)
Hydrostatic pressure (hρg)
Excess pressure (2S/r)
This simulation demonstrates the pressure differences in bubbles based on the following principles:
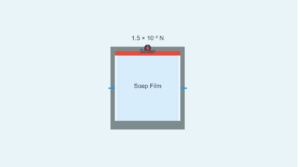
Soap bubble excess pressure: P = 4S/r
A soap bubble has two liquid surfaces (inside and outside), so the excess pressure is twice that of a single surface.
Air bubble excess pressure: P = 2S/r
An air bubble in liquid has only one liquid surface, so the excess pressure is half that of a soap bubble.
Total pressure in air bubble: P = P₀ + hρg + 2S/r
Where P₀ is atmospheric pressure, h is depth, ρ is liquid density, and g is gravity.
Key observations:
- Smaller bubbles have higher excess pressure (inversely proportional to radius)
- Deeper air bubbles experience greater hydrostatic pressure
- Surface tension directly affects the excess pressure in bubbles