Thermodynamics Concepts Simulation
Visualizing key thermodynamics principles through interactive demonstrations
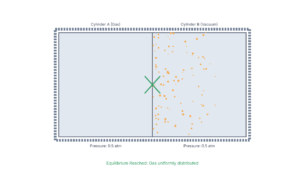
Question (a): Thermal Contact Equilibrium
Why don't two bodies at different temperatures necessarily settle to the mean temperature when brought in thermal contact?
Explanation
The equilibrium temperature depends on the heat capacities of the bodies:
Where:
- Q = heat transferred
- m = mass
- c = specific heat capacity
- ΔT = temperature change
The equilibrium temperature is the weighted average based on heat capacities:
Only when m₁c₁ = m₂c₂ does T_eq = (T₁ + T₂)/2
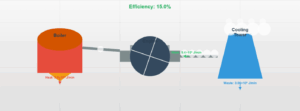
Question (b): Coolant Specific Heat
Why should coolants in plants have high specific heat?
Explanation
Specific heat capacity (c) determines how much heat a substance can absorb per unit mass:
A high specific heat coolant can:
- Absorb more heat with smaller temperature rise
- Maintain more stable temperatures
- Require less coolant flow for same cooling effect
Water (c = 4186 J/kg°C) is ideal compared to mercury (c = 140 J/kg°C)
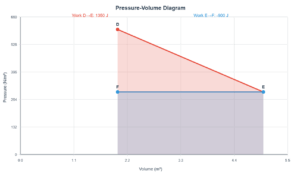
Question (c): Car Tyre Pressure
Why does air pressure in car tyres increase during driving?
Explanation
According to the Ideal Gas Law:
Where:
- P = pressure
- V = volume (constant in tyre)
- n = moles of gas
- R = gas constant
- T = temperature
During driving:
- Friction heats the tyre
- Air temperature increases
- Pressure increases proportionally (Charles' Law: P ∝ T)
Question (d): Harbor vs. Desert Climate
Why is a harbor town's climate more temperate than a desert at the same latitude?
Explanation
Water has a high specific heat capacity (4186 J/kg°C vs. ~800 J/kg°C for sand):
- Water absorbs/releases heat slowly, moderating temperatures
- High humidity increases apparent temperature (heat index)
- Evaporation cools the air near water bodies
Deserts experience:
- Large diurnal temperature swings
- Low humidity makes temperatures feel more extreme
- No water buffer to absorb/release heat