Bernoulli's Principle Model
Random Water Particle Flow Simulation
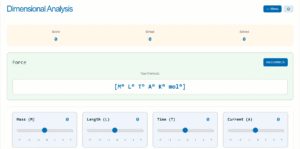
Flow Properties
2.0
120
Pipe Geometry
1.0
0.5
Pressure Difference
0 Pa
Wide Section Velocity
2.55 m/s
Narrow Section Velocity
10.19 m/s
Bernoulli's Equation
P₁ + ½ρv₁² + ρgh₁ = P₂ + ½ρv₂² + ρgh₂
Bernoulli's principle states that an increase in the speed of a fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in static pressure or a decrease in the fluid's potential energy.
In this bernoulli's principle model, water flows through a pipe with a constriction. As the pipe narrows, the fluid velocity increases in the narrow section, causing a pressure drop according to Bernoulli's equation.
The equation demonstrates the conservation of energy in fluid flow, where:
- P is the fluid pressure
- ρ is the fluid density (1000 kg/m³ for water)
- v is the fluid velocity
- g is gravity (9.81 m/s²)
- h is the height above a reference point