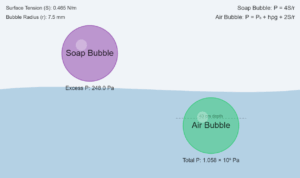
Submarine Pressure at Depth
Example
Question:
At a depth of 1000 m in an ocean
(a) What is the absolute pressure?
(b) What is the gauge pressure?
(c) Find the force acting on the window of area \(20\,\mathrm{cm} \times 20\,\mathrm{cm}\) of a submarine at this depth, the interior of which is maintained at sea-level atmospheric pressure.
(The density of sea water is \(1.03 \times 10^3\,\mathrm{kg\,m^{-3}}\), \(g = 10\,\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}\).)
Solution:
(a) Here \(h = 1000\,\mathrm{m}\), \(\rho = 1.03 \times 10^3\,\mathrm{kg\,m^{-3}}\).
Absolute pressure:
\[
P = P_a + \rho g h
\]
\[
= 1.01 \times 10^5\,\mathrm{Pa} + 1.03 \times 10^3\,\mathrm{kg\,m^{-3}} \times 10\,\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}} \times 1000\,\mathrm{m}
\]
\[
= 104.01 \times 10^5\,\mathrm{Pa} \approx 104\,\mathrm{atm}
\]
(b) Gauge pressure is:
\[
P_g = P - P_a = \rho g h
\]
\[
P_g = 1.03 \times 10^3\,\mathrm{kg\,m^{-3}} \times 10\,\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}} \times 1000\,\mathrm{m}
= 103 \times 10^5\,\mathrm{Pa} \approx 103\,\mathrm{atm}
\]
(c) The pressure outside the submarine is \(P = P_a + \rho g h\) and the pressure inside is \(P_a\). Hence, the net pressure acting on the window is gauge pressure, \(P_g = \rho g h\). The area of the window is \(A = 0.04\,\mathrm{m}^2\). The force on it is:
\[
F = P_g A = 103 \times 10^5\,\mathrm{Pa} \times 0.04\,\mathrm{m}^2 = 4.12 \times 10^5\,\mathrm{N}
\]
Pressure Calculations
Absolute Pressure: 104.01 × 10⁵ Pa (104 atm)
Gauge Pressure: 103 × 10⁵ Pa (103 atm)
Force on Window: 4.12 × 10⁵ N