2D Gravity Simulation: Earth's Gravitational Field
Discover how gravitational forces work with our interactive 2d gravity simulation. Visualize how gravitational acceleration changes with distance from Earth's center, perfect for physics students and educators.
How to Use This Simulation
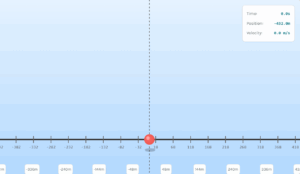
Use the slider below to change your position relative to Earth's center. Watch how gravity changes in real-time on both the Earth visualization and the graph. The left panel shows your position, while the right panel graphs the gravitational force at different distances.
💡 Quick Tip: Try moving from Earth's center to beyond the surface to see how gravity behaves differently inside vs. outside our planet!
How This 2D Gravity Simulation Works
🎮 Control Panel
🔬 Physics Principles Explained
Gravitational Force Outside Earth
When you're outside Earth (distance ≥ Earth's radius), gravity follows Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation. The gravitational force decreases with the square of the distance from Earth's center. This means at twice Earth's radius, gravity is only 1/4 as strong as at the surface. This 2d gravity simulation clearly shows this inverse-square relationship.
Gravitational Force Inside Earth
Inside Earth (distance < Earth's radius), something interesting happens! Gravity decreases linearly as you move toward the center. This occurs because only the mass enclosed within your current radius contributes to the gravitational force, while the outer layers effectively cancel out according to the Shell Theorem.
📋 Key Concepts Summary
Essential Physics Facts
- Earth's mass: 5.972 × 10²⁴ kg
- Earth's radius: 6,371 km
- Gravitational constant: 6.674 × 10⁻¹¹ N·m²/kg²
- Surface gravity: 9.81 m/s² (1.00g)
- Gravity at Earth's center: 0 m/s²
- Outside Earth: Gravity ∝ 1/r² (inverse square law)
- Inside Earth: Gravity ∝ r (linear decrease to center)