Magnetic Field from Current-Carrying Wire
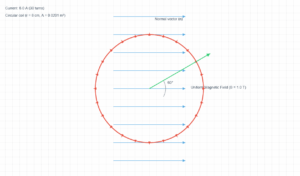
Value: 90 A
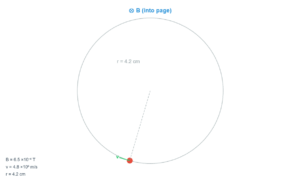
Value: 1.5 m
Physics Explanation
A current-carrying wire produces a magnetic field around it. The magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance r from a long straight wire carrying current I is given by:
B = (μ₀ × I) / (2π × r)
Where μ₀ is the permeability of free space (4π × 10⁻⁷ T·m/A).
The direction of the magnetic field is determined by the right-hand rule: point your thumb in the direction of the current, and your fingers curl in the direction of the magnetic field.
In this simulation, the current flows east to west (left to right), so the magnetic field below the wire points south (into the screen).