Cesium Photoelectric Effect
Metal Properties
Value: 2.14 eV
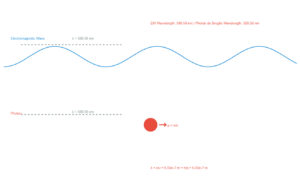
Incident Light
Value: 6.0 ×10¹⁴ Hz
Photoelectric Effect Theory
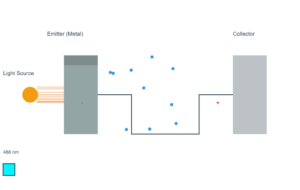
When light of sufficient frequency shines on a metal surface, electrons can be ejected. This is called the photoelectric effect.
Key Equations
Photon Energy: E = hν
Where:
- h = Planck's constant (6.626 × 10⁻³⁴ J·s)
- ν = frequency of incident light
Maximum Kinetic Energy: Kmax = hν - φ
Where φ is the work function of the metal.
Stopping Potential: eV₀ = Kmax
Electron Speed: v = √(2Kmax/me)
Current Simulation Results
Work Function (φ): 2.14 eV
Photon Energy (hν): 2.48 eV
Max Kinetic Energy: 0.34 eV
Stopping Potential: 0.34 V
Max Electron Speed: 3.49 × 10⁵ m/s