Quantum Wave-Particle Duality
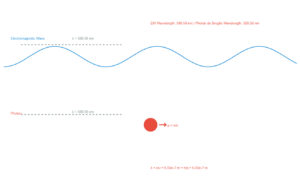
Explore the fundamental concept of wave-particle duality through the de Broglie hypothesis. This simulation visualizes how matter exhibits both particle and wave characteristics, with wavelength calculated by λ = h/(m·v) where h is Planck's constant (6.626×10⁻³⁴ J·s).
0 m/s
1000 m/s
1000 m/s
Quantum Parameters
Selected Object
Bullet
Mass
0.040 kg
Velocity
1000 m/s
Wavelength
1.65×10⁻³⁵ m
λ = h / (m·v) = 6.626×10⁻³⁴ / (0.040 × 1000) = 1.65×10⁻³⁵ m
Note: The wavelength is scaled up by 10³⁰ for visualization purposes.