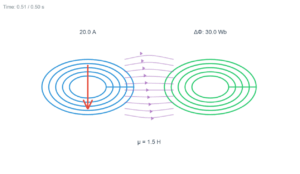
Lenz's Law Simulation
Figure shows planar loops of different shapes moving out of or into a region of magnetic field directed normal to the plane of the loop (away from reader). Determine the direction of induced current using Lenz's law.
The direction of induced current always opposes the change in magnetic flux that produces it.
Interactive Simulation
Select a loop shape and observe the induced current direction as it moves through the magnetic field:
Example
Question:
Figure 6.7 shows planar loops of different shapes moving out of or into a region of a magnetic field which is directed normal to the plane of the loop away from the reader. Determine the direction of induced current in each loop using Lenz’s law.
Solution:
(i) Magnetic flux through rectangular loop abcd increases (loop moves into field region). Induced current must flow along path bcdadab (i.e. circular: b→c→d→a→b), so as to oppose increasing flux.
(ii) Due to outward motion, flux through triangular loop abc decreases. Induced current flows along bacb (b→a→c→b), to oppose loss of flux.
(iii) As magnetic flux decreases when irregular loop abcd leaves field region, induced current flows along cdabc (c→d→a→b→c), to oppose the flux reduction.
Note: No induced current while loops are entirely inside or outside the magnetic field region.
When the rectangular loop enters the field, the increasing flux induces a current that flows to oppose this change (clockwise in this case).