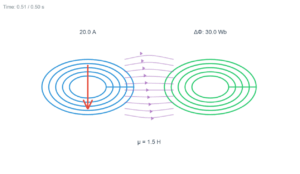
Electromagnetic Induction Simulation
Example 6.3: Rotating Coil in Earth's Magnetic Field
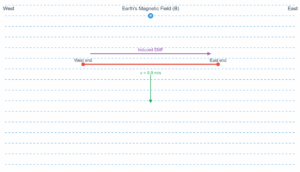
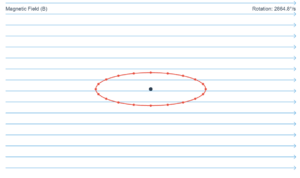
A circular coil of radius 10 cm, 500 turns and resistance 2 Ω is placed with its plane perpendicular to the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field. It is rotated about its vertical diameter through 180° in 0.25 s.
Example
Question:
A circular coil of radius 10 cm, 500 turns and resistance 2 Ω is placed with its plane perpendicular to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field. It is rotated about its vertical diameter through 180° in 0.25 s. Estimate the magnitudes of the emf and current induced in the coil. Horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at the place is \(3.0 \times 10^{-5}\) T.
Solution:
Initial flux through the coil: \[ \Phi_{B(\text{initial})} = BA \cos\theta = 3.0 \times 10^{-5} \times (\pi \times 10^{-2}) \times \cos 0^\circ = 3\pi \times 10^{-7}\ \text{Wb} \] Final flux after rotation: \[ \Phi_{B(\text{final})} = 3.0 \times 10^{-5} \times (\pi \times 10^{-2}) \times \cos 180^\circ = -3\pi \times 10^{-7}\ \text{Wb} \] Estimated induced emf: \[ \epsilon = N \frac{\Delta\Phi}{\Delta t} = 500 \times \frac{6\pi \times 10^{-7}}{0.25} \] \[ = 3.8 \times 10^{-3}\ \text{V} \] Induced current: \[ I = \frac{\epsilon}{R} = \frac{3.8 \times 10^{-3}\ \text{V}}{2\ \Omega} = 1.9 \times 10^{-3}\ \text{A} \] Note: These magnitudes are estimated and depend upon the speed of rotation at the particular instant.