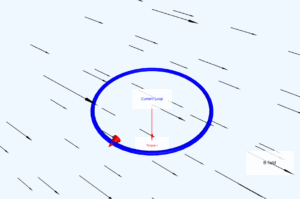
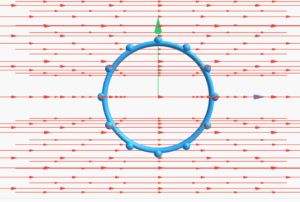
Electron Path in Magnetic Field
Example 4.3: Electron's Circular Motion
This simulation demonstrates an electron's circular path in a perpendicular magnetic field.
Example
Question:
What is the radius of the path of an electron of mass \(9 \times 10^{-31}\,\text{kg}\) and charge \(1.6 \times 10^{-19}\,\text{C}\) moving at a speed of \(3 \times 10^7\,\text{m}\,\text{s}^{-1}\) in a magnetic field of \(6 \times 10^{-4}\,\text{T}\) perpendicular to its velocity? Calculate its frequency. Calculate its energy in keV. (1 eV = \(1.6 \times 10^{-19}\,\text{J}\).)
Solution:
Using Eq. (4.5):
\[
r = \frac{mv}{qB}
= \frac{9 \times 10^{-31}\,\text{kg} \times 3 \times 10^7\,\text{m}\,\text{s}^{-1}}{1.6 \times 10^{-19}\,\text{C} \times 6 \times 10^{-4}\,\text{T}}
= 28 \times 10^{-2}\,\text{m} = 28\,\text{cm}
\]
\[
v = \frac{v}{2\pi r}
= 17 \times 10^6\,\text{s}^{-1} = 17\,\text{MHz}
\]
\[
E = \frac{1}{2} mv^2 = \frac{1}{2} \times 9 \times 10^{-31}\,\text{kg} \times 9 \times 10^{14}\,\text{m}^2\,\text{s}^{-2}
= 4 \times 10^{-16}\,\text{J}
= 2.5\,\text{keV}
\]