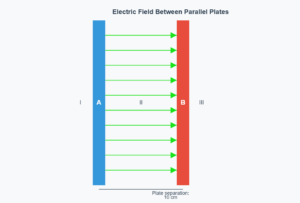
Electric Field Particle Simulation
Example
Question:
An electron falls through a distance of \(1.5\,\mathrm{cm}\) in a uniform electric field of magnitude \(2.0 \times 10^4\,\mathrm{N\,C}^{-1}\) [Fig. 1.10(a)]. The direction of the field is reversed keeping its magnitude unchanged and a proton falls through the same distance [Fig. 1.10(b)]. Compute the time of fall in each case. Contrast the situation with that of ‘free fall under gravity’.
Solution:
In Fig. 1.10(a), the field is upward, so the negatively charged electron experiences a downward force of magnitude \(eE\), where \(E\) is the magnitude of the electric field.
The acceleration of the electron is
\[
a_e = \frac{eE}{m_e}
\]
where \(m_e\) is the mass of the electron.
Starting from rest, the time required by the electron to fall through a distance \(h\) is
\[
t_e = \sqrt{\frac{2h}{a_e}} = \sqrt{\frac{2h m_e}{eE}}
\]
For \(e = 1.6 \times 10^{-19}\,\mathrm{C}\), \(m_e = 9.11 \times 10^{-31}\,\mathrm{kg}\),\\
\(E = 2.0 \times 10^4\,\mathrm{N\,C}^{-1}\), \(h = 1.5 \times 10^{-2}\,\mathrm{m}\),
\[
t_e = 2.9 \times 10^{-9}\,\mathrm{s}
\]
In Fig. 1.10(b), the field is downward, and the positively charged proton experiences a downward force of magnitude \(eE\). The acceleration of the proton is
\[
a_p = \frac{eE}{m_p}
\]
where \(m_p\) is the mass of the proton; \(m_p = 1.67 \times 10^{-27}\,\mathrm{kg}\).\\
The time of fall for the proton is
\[
t_p = \sqrt{\frac{2h}{a_p}} = \sqrt{\frac{2h m_p}{eE}}
= 1.3 \times 10^{-7}\,\mathrm{s}
\]
Thus, the heavier particle (proton) takes a greater time to fall through the same distance. This is in contrast to 'free fall under gravity', where the time of fall is independent of the mass of the body.
To justify neglecting gravity, calculate the acceleration of the proton in the electric field:
\[
a_p = \frac{eE}{m_p} = \frac{(1.6 \times 10^{-19}\,\mathrm{C}) \times (2.0 \times 10^4\,\mathrm{N\,C}^{-1})}{1.67 \times 10^{-27}\,\mathrm{kg}} = 1.9 \times 10^{12}\,\mathrm{m\,s}^{-2}
\]
This is enormous compared to the value of \(g\) (\(9.8\,\mathrm{m\,s}^{-2}\)), so the effect of acceleration due to gravity can be ignored.
Simulation Information
This simulation demonstrates how electrons and protons fall through a uniform electric field. The field direction can be toggled to show both scenarios from Example 1.7.
Time of fall: 2.9 × 10-9 s
Acceleration: 3.5 × 1015 m/s²
Time of fall: 1.3 × 10-7 s
Acceleration: 1.9 × 1012 m/s²