Aluminum Cube Shear Deformation Simulation
Where:
η = Shear modulus (25 GPa for aluminum)
F = Force (weight = mass × gravity)
A = Area of the face (L²)
L = Edge length of cube
Δx = Vertical deflection
Aluminum Properties
Shear modulus (η): 25 GPa
Density: 2.7 g/cm³
Typical applications: Aircraft components, cans, foils
Explanation
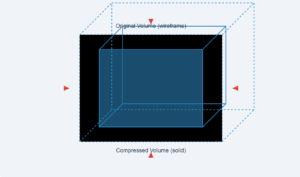
This simulation demonstrates the shear deformation of an aluminum cube when one face is fixed to a wall and a mass is attached to the opposite face.
Shear modulus (η) describes a material's response to shear stress, which is a force applied parallel to a surface. In this case, the weight of the attached mass creates a shear force on the cube.
The vertical deflection (Δx) is calculated by the formula Δx = (F·L)/(η·A), where F is the force (mass × gravity), L is the edge length, and A is the area of the face (L²).
Adjust the cube size and attached mass to see how these parameters affect the deformation. Note that the deformation is exaggerated in the visualization for clarity.