Bulk Modulus Comparison
Visualizing the compressibility of water versus air
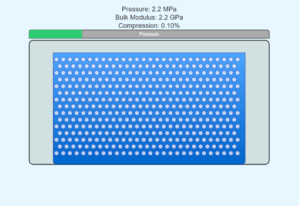
Bulk Modulus Explained
Bulk modulus measures a substance's resistance to uniform compression. It's defined as:
B = -V (ΔP/ΔV)
Where:
- B = Bulk modulus (Pa)
- V = Initial volume (m³)
- ΔP = Pressure change (Pa)
- ΔV = Volume change (m³)
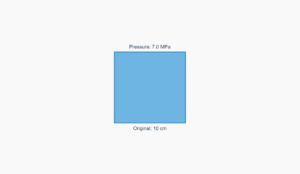
Water
2.026 × 10⁹ Pa
Highly incompressible
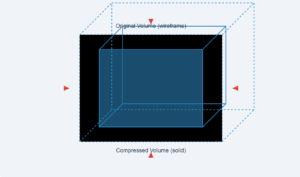
Air
1 × 10⁵ Pa
Highly compressible
The ratio of bulk moduli is:
2.026 × 10⁴
Why is water so much less compressible than air?
Water molecules are packed tightly together with strong intermolecular forces, making it resistant to compression. Air molecules are far apart with weak interactions, allowing easy compression.