Center of Mass Motion
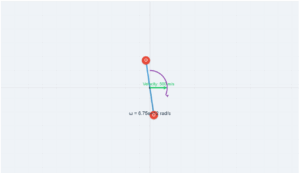
Child running on a uniformly moving trolley
Trolley Speed
1.0
m/s
Child Speed
0.0
m/s (relative)
Center of Mass Speed
1.0
m/s
Trolley
Child
Center of Mass
Physics Explanation
This simulation demonstrates the motion of the center of mass (COM) of a system consisting of a trolley and a child.
Problem Statement: A child sits stationary at one end of a long trolley moving uniformly with speed V on a smooth horizontal floor. If the child gets up and runs about on the trolley, what is the speed of the COM of the (trolley + child) system?
Key Concepts:
- The COM velocity of a system depends only on external forces (Newton's First Law)
- Internal forces (like the child pushing on the trolley) don't affect the COM motion
- With no net external force, the COM velocity remains constant
Mathematical Explanation:
The velocity of the center of mass is given by:
v_cm = (m_trolley * v_trolley + m_child * v_child) / (m_trolley + m_child)
When the child runs:
- The child's motion creates equal and opposite internal forces on the trolley
- These forces cancel out in the COM calculation
- The COM velocity remains unchanged at its initial value
Conclusion: The child's running produces no effect on the velocity of the center of mass of the trolley-child system.