Advanced Resonance Tube Physics Simulation
Physics of Resonance in Closed-Open Tubes
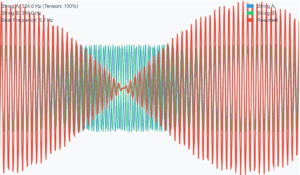
This simulation demonstrates how resonance occurs in air columns with one closed end (piston) and one open end. The system produces only odd harmonics due to the boundary conditions:
L = (2n - 1)λ/4 (n = 1, 2, 3,...)
Key Boundary Conditions:
- Closed end (piston): Displacement node (particles cannot move) and pressure antinode
- Open end: Displacement antinode (maximum particle motion) and pressure node
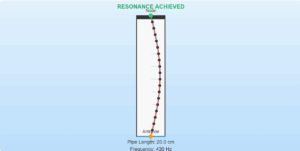
Problem Solution Analysis:
- Given resonance lengths: 25.5 cm (1st harmonic) and 79.3 cm (3rd harmonic)
- For fundamental mode (n=1): L₁ = λ/4 → λ = 4 × 0.255 m = 1.02 m
- Speed of sound: v = fλ = 340 Hz × 1.02 m = 346.8 m/s
- For 3rd harmonic (n=2): L₃ = 3λ/4 = 0.793 m (matches given data)
- Theoretical speed at 20°C: v = 331 + (0.6 × 20) = 343 m/s (close to our calculation)
Temperature Effect: The speed of sound in air varies with temperature:
v = 331 + (0.6 × T) m/s (T in °C)