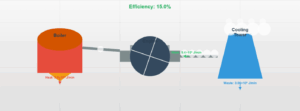
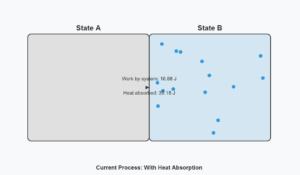
Thermodynamic Process Work Simulation
Work Done Calculation from D → E → F Process
Initial State (D)
200
600
800
1.0
2.0
3.0
Final State (E)
200
300
800
3.0
5.0
7.0
Work Done (D→E)
450 J
Area under D→E curve
W = ½ × (P₁ + P₂) × ΔV
W = ½ × (P₁ + P₂) × ΔV
Work Done (E→F)
0 J
Area under E→F isobar
W = P × ΔV
W = P × ΔV
Physics Theory
The work done by a thermodynamic system during a process equals the area under the pressure-volume (PV) curve. For the D→E→F process:
D → E: Linear process → W = Area of triangle DEF = ½ × (P_D - P_E) × (V_E - V_D)
E → F: Isobaric process → W = P_E × (V_F - V_E) = P_E × (V_D - V_E)
The total work done is the sum of work done in both processes:
W_total = W_D→E + W_E→F
This simulation demonstrates how the work done corresponds to the area under the PV curve, with the D→E process forming a triangle and the E→F process forming a rectangle (or negative rectangle when volume decreases).