Ideal Gas Thermometer Simulation
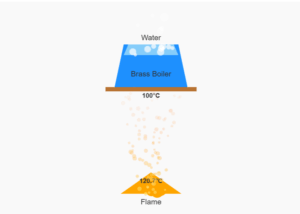
Measuring the Melting Point of Sulphur
Experimental Parameters
Thermometer Settings
Thermometer A (O₂)
Current pressure: 1.797 ×10⁵ Pa
Thermometer B (H₂)
Current pressure: 0.287 ×10⁵ Pa
Physics Theory
The ideal gas thermometer works on the principle that the pressure of a gas at constant volume is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. This relationship is described by:
Where P is pressure, T is absolute temperature, and k is a constant. The triple point of water (273.16 K) serves as the reference temperature. For any other temperature T₁:
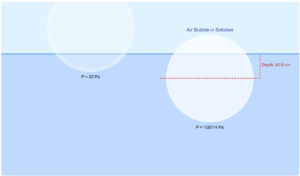
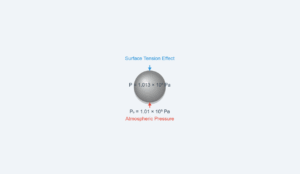
In reality, gases deviate from ideal behavior due to intermolecular forces and finite molecular volume. The discrepancy between different gas thermometers can be minimized by extrapolating measurements to zero pressure where all gases behave ideally.
This simulation demonstrates how different gases (O₂ vs H₂) give slightly different temperature readings for the same physical temperature due to their different non-ideal behaviors.